In modern days, technology took an important place in eve-ryone’s life and phones are become an essential part of our daily routine. You can find several apps available which sat-isfy your daily needs and enables you to keep engages so-cially as well. So, app development as profession is on boom.
In this article we are going to talk about how can one start, how to build Android apps.
how to develop android application is a tough task, but it can open up a world of possibilities. There are possibilities that you develop the next big hit app.
Gather tools required for Android development
The first and foremost step is to create environment for the android development, it doesn’t matter which operating sys-tem you are using, weather its Windows, Mac or Linux, you can setup environment for android development anywhere.
Android Studio is the official Integrated Development Envi-ronment (IDE) for Android app development, based on Intel-liJ IDEA. On top of IntelliJ's powerful code editor and devel-oper tools, Android Studio offers even more features that enhance your productivity when building Android apps
Fortunately, set up is very simple and you only need to follow along with the instructions on the screen.
Let’s begin with a new project
No as you have Android studio install on your machine,
the next step is to start a new project in android studio. The process for
creating a new project is very straight forward, android studio will prompt you
to create a new project or use existing project.
You just need to go to File > New > New
Project. You will now be asked to select a “Project Template.” This will
autoload the preconfigured code and UI elements based on Template.
After this, when the project is loaded, you will see view like below figure:
Now in above figure Name you application, define the package name(Package name could be anything unique, typically like “com.facebook.xxx”), path of the project on your location computer, development language i.e Kotlin or Java and define Minimum sdk.
Language selection
Kotlin is the preferred language for Android development in 2021. Both Java and Kotlin can be used to build performant, useful applications, but Google’s libraries, tooling, documentation, and learning resources continue to embrace a Kotlin-first approach; making it the better language for Android today.
Java
Java is an
object-oriented programming language. It was released in 1995 by the Sun
Microsystems. This company is the property of Oracle. Most Java elements are
available in open-source. A large part of the Android apps and the Android
itself are based on Java. In 2020 Java is the 3rd most popular language on
GitHub.
Kotlin
People from JetBrains launched Kotlin to make coding in Java more productive. Kotlin became an official programming language in 2018. It is the programming language that runs on JVM. JVM means Java Virtual Machine. Besides that, the Kotlin can be compiled into JavaScript and run in browsers. It is possible to code on Kotlin/Native. Android developers can use IDE to build cross-platform apps.
SDK Version
minSdkVersion: an integer designating the minimum API Level required for the application to run. The Android system will prevent the user from installing the application if the system's API Level is lower than the value specified in this attribute.
targetSdkVersion: an integer designating the maximum API Level on which the application is designed to run. In Android 1.5, 1.6, 2.0, and 2.0.1, the system checks the value of this attribute when installing an application and when re-validating the application after a system update. In either case, if the application's maxSdkVersion attribute is lower than the API Level used by the system itself, then the system will not allow the application to be installed. In the case of re-validation after system update, this effectively removes your application from the device.
maxSdkVersion: an integer designating the maximum API Level on which the application is designed to run. In Android 1.5, 1.6, 2.0, and 2.0.1, the system checks the value of this attribute when installing an application and when re-validating the application after a system update. In either case, if the application's maxSdkVersion attribute is lower than the API Level used by the system itself, then the system will not allow the application to be installed. In the case of re-validation after system update, this effectively removes your application from the device.
Android Application File Structure
It is very
important to know about the basics of Android Studio’s file structure. In this
article, some important files/folders, and their significance is explained for
the easy understanding of the Android studio work environment.
In the
below image, several important files are marked:
All of the files marked in the above image are explained below in brief:
AndroidManifest.xml:
Every project in Android includes a manifest file, which is AndroidManifest.xml, stored in the root directory of its project hierarchy. The manifest file is an important part of our app because it defines the structure and metadata of our application, its components, and its requirements.
This file
includes nodes for each of the Activities, Services, Content Providers and
Broadcast Receiver that make the application and using Intent Filters and
Permissions, determines how they co-ordinate with each other and other
applications.
A typical
AndroidManifest.xml file looks like:
Java:
The Java folder contains the Java
source code files. These files are used as a controller for controlled UI
(Layout file). It gets the data from the Layout file and after processing that
data output will be shown in the UI layout. It works on the backend of an
Android application.
drawable:
A Drawable folder contains
resource type file (something that can be drawn). Drawables may take a variety
of file like Bitmap (PNG, JPEG), Nine Patch, Vector (XML), Shape, Layers,
States, Levels, and Scale.
layout:
A layout defines the visual
structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an Android application. This
folder stores Layout files that are written in XML language. You can add
additional layout objects or widgets as child elements to gradually build a
View hierarchy that defines your layout file.
Below is a
sample layout file:
mipmap:
Mipmap folder contains the Image
Asset file that can be used in Android Studio application. You can generate the
following icon types like Launcher icons, Action bar and tab icons, and
Notification icons.
colors.xml:
colors.xml file contains color
resources of the Android application. Different color values are identified by
a unique name that can be used in the Android application program.
Below is a
sample colors.xml file:
strings.xml:
The strings.xml file contains
string resources of the Android application. The different string value is
identified by a unique name that can be used in the Android application
program. This file also stores string array by using XML language.
Below is a
sample colors.xml file:
styles.xml:
The styles.xml file contains resources
of the theme style in the Android application. This file is written in XML
language.
Below is a
sample styles.xml file:
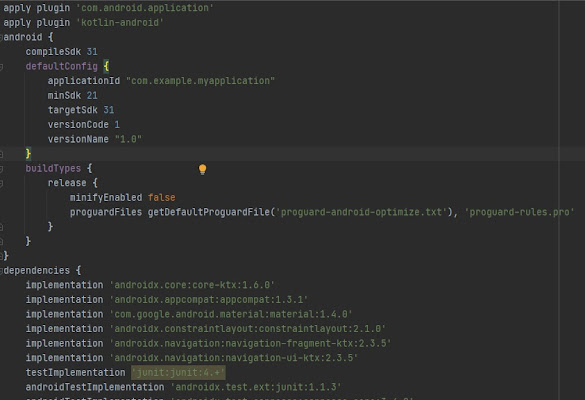
build.gradle(Module: app):
This defines the
module-specific build configurations. Here you can add dependencies what you
need in your Android application.
Test Run your app
The next step is to launch your app by clicking on
play icon in the bar on top right corner. It should look like this.









Comments
Post a Comment